Cameras
A LEGION Camera is a rectangular boundary used to frame interesting regions of the model for visual analysis. Cameras provide focussed coverage of such regions by excluding model space outside the Camera boundary.
Motivation
The primary use case is recording videos, images, and screen outputs, using the Timeline. There’s also a secondary use: switching the screen view to a specific region, either manually (right-click in the Workspace and select Set Active Camera…) or during recording and playback (see Timeline Screen Camera Track).
Cameras address these situations:
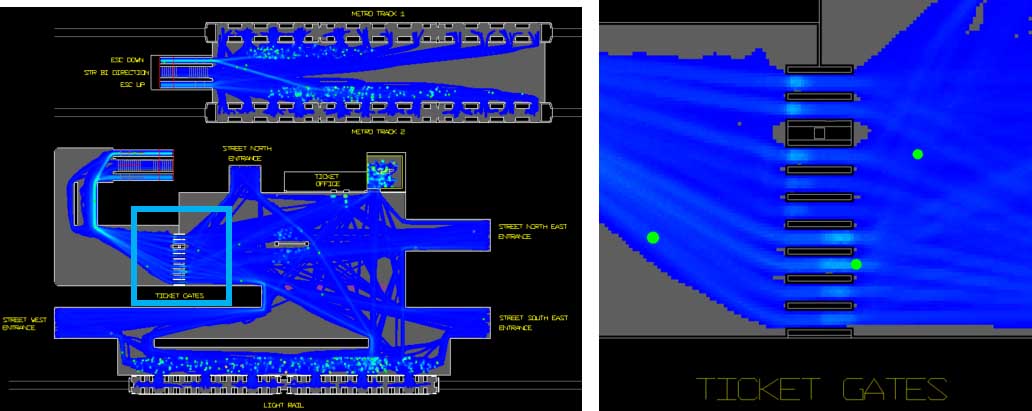
- Every model has interesting regions requiring detailed observation, and mundane regions where pedestrians simply transit between objectives.
- Pixel dimensions of the
LEGION workspace may not align with desired output dimensions, especially when
graphs and map legends are visible.
- Outputs should be
independent of workspace dimensions.
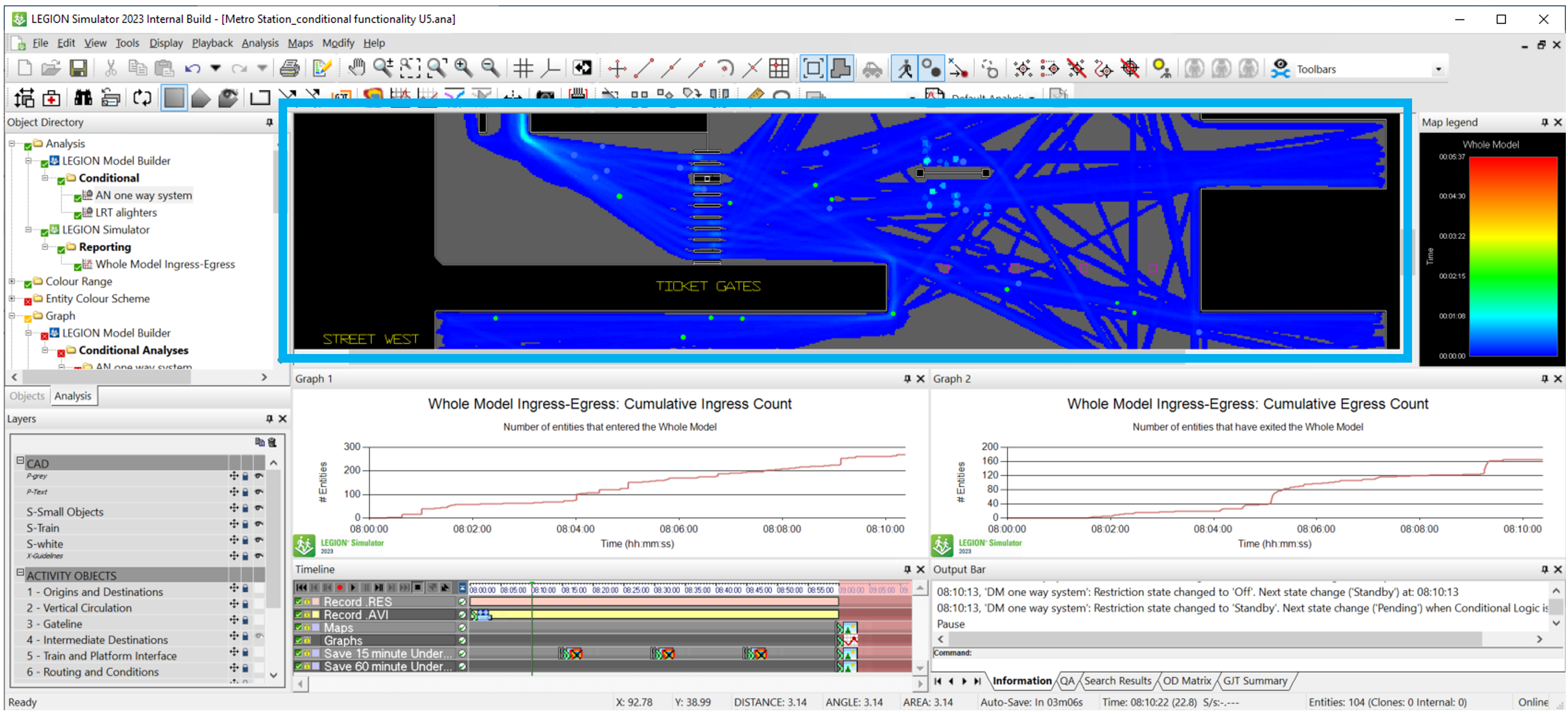
- For example, a standard image or video output dimension is 1920 x 1080 pixels, so it fits neatly on 16:9 full HD display. Yet, in the LEGION workspace view below (blue box) the workspace is clearly not this size or aspect ratio (in fact it’s 1429 x 449 pixels, an approximate 3.18:1 ratio; not friendly dimensions for video or images).
- Outputs should be
independent of workspace dimensions.
- Consistency of outputs. It is helpful for all outputs to have a similar arrangement, as this makes for easier viewing and consumption by stakeholders.
LEGION Simulator supports unlimited Cameras. Camera boundaries may overlap.
Output and Visualisations Which Depend on Cameras
These outputs and visualisations depend on Cameras:
LEGION Camera Concepts
- Whole Model Camera: A system-defined Camera that encompasses the entire model area and automatically updates to model content changes. The aspect ratio for this Camera can be modified, but the Field of View cannot.
- Camera Coverage: The area inside the Camera boundary, which is based on two related parameters:
- Maintaining Aspect Ratio: When a Camera’s aspect ratio stays constant while its Field of View is modified. The size changes but the shape does not. Changing one Field of View dimension automatically updates the other, the aspect ratio does not change.
- Centre Lock: The Camera’s centre point does not change when its aspect ratio or Field of View is modified. Keeps the Camera focussed on the interesting region while its size and/or shape is modified.